-
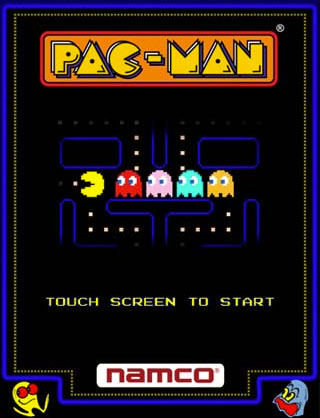
Pro Pool originated in December with 800 units being fabricated. This add-a-ball machine was designed by Ed Krynski with artwork by Gordon Morison. Two replay versions of the game were also made: a two-player version called Big Shot and a four-player version called Hot Shot. Obviously the theme of this game is the game of pool. The playfield is symmetrical and the way to win extra balls is by completing the left and/or right drop target battery. Doing so will lift the left and/or right wow rollovers for this award. The drop targets reset once the sequences are completed. Of course, an operator-adjusted score is another way to score a couple of balls. Back in the ‘70s, multiple balls or replays could be achieved on the game. Today, one free game on a current solid-state game is the common win. Operators have made it harder to achieve free games today as free games yield no income and only result in down time for the machine to earn coins in the till.Gottlieb Pop-A-Card was another classic ‘70s playfield designed by Ed Krynski with artwork by Gordon Morison. Only 825 of these units were made. The replay version of the game was called Drop–A-Card which, as usual, was a much higher produced machine. The open playfield of this game gives ample room for scoring the three banks of drop targets. To win free balls with this game, you have to either complete the 2, 3, 4, and 5 targets, or the 6, 7, 8, and 9 targets…or the 10, J, Q, K, and Ace targets. The first two options light the wow feature to award free balls during that ball in play. If you hit the 10 thru Ace targets to completion, four rollovers light up to score extra balls. Of course, score is another way to score more balls.Atari PONG was released in June 1972 and is the first commercially successful video game and is based on a simple two-dimensional graphical representation of a tennis-like game. Players use paddles to hit a ball back and forth on a black and white screen. Pong was the first game developed by Atari Inc., by Nolan Bushnell and Ted Dabney. Pong (marketed as PONG) is one of the earliest arcade video games, and is a tennis sports game featuring simple two-dimensional graphics. The player controls an in-game paddle by moving it vertically across the left side of the screen, and can compete against either a computer controlled opponent or another player controlling a second paddle on the opposing side. Players use the paddles to hit a ball back and forth. The aim is for a player to earn more points than the opponent; points are earned when one fails to return the ball to the other. Pong consistently earned four times more revenue than other coin-operated machines, which resulted in an increase in the number of orders Atari received. This provided Atari with a steady source of income; the company sold the machines at three times the cost of production. By 1973, the company had filled 2,500 orders, and, at the end of 1974, sold more than 8,000 units.[20] The arcade cabinets have since become collector’s items with the cocktail-table version being the rarest. Atari eventually sold more than 35,000 units, however, many more imitations were produced by competitors.Gameplay of Pole Position. In this game, the player controls a Formula One race car, and has to complete a time trial lap within a certain amount of time (between 90 and 120 seconds) to qualify for an F1 race at the Fuji Racetrack. After qualifying, the player races against seven other CPU-controlled cars in a championship race (but if he or she does not qualify, the car will stay on the track until the timer runs out). The player must also avoid going off the road so that he or she will not crash into the billboards. Pole Position was the first racing video game to feature a track based on a real racing circuit. It was also the first game to feature a qualifying lap, requiring the player to complete a time trial before they can compete in Grand Prix races. Once the player has qualified, they must complete the race in the time allowed, avoiding collisions with CPU-controlled opponents and billboards along the sides of the track. The game’s publisher Atari publicized the game for its “unbelievable driving realism” in providing a Formula 1 experience behind a racing wheel. The game’s graphics featured full-color landscapes with scaling sprites, including race cars and other signs, and a pseudo-3D, third-person, rear perspective view of the track, with its vanishing point swaying side to side as the player approaches corners, accurately simulating forward movement into the distance.The last game of ’65 is a two-player add-a-ball game. It was designed by Ed Krynski with art by Roy Parker. A replay model also exists by the name of Paradise. Production run was a meager 265 units; the replay game had 2,100 units fabricated. The animated backglass on this game contains a dancing hula girl. When extra balls are won, they are represented as beach balls on the backglass. If you complete the sequence A, B, C, and D in that order, a free ball is your reward. Roto lights advance and indicate the value of the kickout holes. Points set by the operator award free balls also. An interesting guide rail is on either side of the flipper drains, a variation on a theme. This game is very rare due to its low production numbers.This solid-state game was very popular when it was released and has a lot of smooth shots to complete. It was designed by Jim Patla with artwork by Paul Faris. Production run was 18,250 units. This pre-speaking pinball has Hugh Hefner on its backglass with Bunny Sondra Theodore posing. At the top of the game are four rollover lanes, which advance when hit to a special and advance the bonuses and grotto award. Hitting the five Bunny targets also advance a feature to win extra balls and specials. A unique kickback lane advances with every entrance into it. A five-pack of drop targets also advance certain features on the game. If 20,000 points are made on the bonus system, this point count is carried over to all remaining balls and then some. The nicest shot on the game is going up the right side from the flipper and looping the ball into the grotto. The sound originates from the old TV show “Playboy After Dark.”Gottlieb hatched this add-a-ball machine from the skunkworks in April of the year, designed by Ed Krynski and artwork by Gordon Morison. This single-player machine has a bowling theme and only 715 units were produced at that time. The replay version of the game was called King Pin and many more of these machines were produced. The theme of this game is the drop target completion. By carefully aiming the four inherent flippers on board the playfield, one must try to complete the horizontal row of targets. Doing so will reset the targets and the wow feature activates, giving you a shot at the accomplishment of winning extra balls. Score is another way to pop free balls. The ten drop targets are not so easy to complete and the wow feature advances when you roll over the star rollover. This game is challenging, but a beginner can have ample fun with the machine.This machine was a big hit for Williams with 12,000 machines created. A skill shot starts your adventure with different point values. A three-bank drop target or single right target advances the planets lit in the playfield. If you advance to the lit planet, a free game is your reward. The light grid, if hit when a solo target is lit, opens the visor. Otherwise, hitting all the lights opens the visor. Locking two balls in the “eyes” of the robot starts two-ball multiball. Lock one ball in one eye and shoot for the left solar ramp. Advance the bonus value by making the left ramp loop when the visor is down. This game is fun, challenging and the vocals egg you on throughout your adventure.Photo Booth 2 Strips of Photos – $5 THIS PHOTO BOOTH WAS AT PALACE AMUSEMENTS ! You’re standing in front of the photo booth which operated at Asbury Park’s famous Palace Amusements for nearly three decades. The Palace was a huge indoor entertainment center with hundreds of arcade games and full size rides, including a ferris wheel that extended up through the roof of the building. It was located three blocks south of here at the corner of Cookman Avenue & Kingsley Street, just west of the Casino carousel building. The site is now a parking lot. Installed by Palace owners Edward Lange and Zimel Resnik in the late 1950s or early 1960s, this photo booth delighted thousands of patrons until November 27, 1988 when the Palace closed its doors for the final time. The building sat vacant and decaying for more than 15 years until it was demolished in May 2004, despite massive public opposition and offers from local developers to save and renovate the historic 1888 structure. After the Palace closed the booth was moved to Sandy’s Arcade, which at that time was located in the First Avenue Pavilion on the Asbury Park boardwalk. Today Cubacan Restaurant occupies the arcade’s former space. Sandy’s went out of business in the early 1990s and the photo booth was put up for sale. The offering caught the attention of Slim and Pamela Smith, Jersey Shore natives who had migrated to Vermont but were vacationing near Asbury Park. The Smiths stumbled upon the closed arcade and purchased the photo booth. They moved it 342 miles north to Burlington, Vermont and installed it in their small gift shop known as “Folkheart”. Eventually the machine was moved to a second Folkheart location in the tiny village of Bristol, Vermont where it resided among Nepalese clothing, Himalayan bric-a-brac and various trinkets. For thirteen years the Palace photo booth vended pictures for the Smith’s customers. In 2003 the strobe unit which powers the flash tubes failed, and after several unsuccessful repair attempts the booth sat unused for three years. In December 2006 Folkheart went out of business. Slim and Pamela Smith knew the rich history of their beloved photo booth and wanted to see it preserved, but they could no longer keep it. They generously donated the machine to Save Tillie, a nonprofit organization made up of fans of Asbury Park, the Palace and Bruce Springsteen, dedicated to preservation of Palace artifacts. In early 2007 a Save Tillie volunteer restored the booth at an arcade in New York state, and on May 31, 2007 it was brought back home to Asbury Park. It was installed on the lower level of the Shoppes at the Arcade at 658 Cookman Avenue, where it was lovingly maintained by the nonprofit group for more than six years. In 2013 Save Tillie sold the booth. It was relocated to the Silverball Museum on December 2, 2013, where it will be preserved for the enjoyment of generations to come.It’s probably a very rare person who has never played Pac-Man. Even for those who may have missed it in the 1980s, Pac-Man has been re-made on nearly every video game platform since then. Pac-Man even appeared on the front page of Google (as a playable game) on Pac-Man’s 30th anniversary. However, for those few who are unfamiliar with the game, here are the basics. You, the player, control the yellow, circular Pac-Man using either keyboard arrows or a joystick. The goal is to move Pac-Man around the maze-like screen gobbling up all 240 dots before the four ghosts (sometimes called monsters) get you. The four ghosts are all different colors: Blinky (red), Inky (light blue), Pinky (pink), and Clyde (orange). However, they all turn dark blue when Pac-Man eats one of the four power pellets available on each level; the pellets enable Pac-Man to eat the ghosts. Occasionally, fruit will appear on the screen. If Pac-Man gobbles those up then he earns a point bonus, with different fruit worth different values. While all this is happening, Pac-Man makes a wocka-wocka sound that is nearly as memorable as the yellow character himself. When first launched in Japan by Namco in 1980, the game received a lukewarm response, as Space Invaders and other similar games were more popular at the time. However, the game found far more success in North America. Pac-Man’s success in North America took competitors and distributors completely by surprise in 1980. Marketing executives who saw Pac-Man at a trade show prior to release completely overlooked the game (along with the now-classic Defender), while they looked to a racing car game called Rally-X as the game to outdo that year. The appeal of Pac-Man was such that the game caught on immediately with the public; it quickly became far more popular than anything seen in the game industry up to that point. Pac-Man outstripped Asteroids as the best-selling arcade game in North America, grossing over $1 billion in quarters within a decade, by the end of the 1980s, surpassing the revenues grossed by the highest-grossing film “Star Wars”. The player controls Pac-Man through a maze, eating pac-dots (also called pellets). When all pac-dots are eaten, Pac-Man is taken to the next stage. Between some stages one of three intermission animations plays. Four enemies (Blinky, Pinky, Inky and Clyde) roam the maze, trying to catch Pac-Man. If an enemy touches Pac-Man, a life is lost and the Pac-Man itself withers and dies. When all lives have been lost, the game ends. Pac-Man is awarded a single bonus life at 10,000 points by default.
-
Pro Pool originated in December with 800 units being fabricated. This add-a-ball machine was designed by Ed Krynski with artwork by Gordon Morison. Two replay versions of the game were also made: a two-player version called Big Shot and a four-player version called Hot Shot. Obviously the theme of this game is the game of pool. The playfield is symmetrical and the way to win extra balls is by completing the left and/or right drop target battery. Doing so will lift the left and/or right wow rollovers for this award. The drop targets reset once the sequences are completed. Of course, an operator-adjusted score is another way to score a couple of balls. Back in the ‘70s, multiple balls or replays could be achieved on the game. Today, one free game on a current solid-state game is the common win. Operators have made it harder to achieve free games today as free games yield no income and only result in down time for the machine to earn coins in the till.